背景
周一和队友复盘,发现是个自闭场,开了签到和$L$之后剩下的都不怎么会写了。计算几何没带板子,自己写也白给了。一道找环的思维题也没搞出来,这样下去看来银川要铁(麻了)。
赛后补题,整理一点题解放在这里。
题解
Simone and Graph Coloring
这题看了官方题解,说是线段树二分优化最长下降子序列长度。
开始我也想上线段树乱搞一发,不过队友和我说第二题不太可能搞这种东西。
然后开始口胡算法,队友先是搞了一个$set$维护$upper_bound$,找到大于当前元素的第一个元素$K$,染色为$color[K]+1$。通过了小数据,然后也测了一点构造数据,一交$WA$了,后面发现不能直接这么维护。
此时代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define maxn 1000005
using namespace std;
int t, n, maxx;
int a[maxn], color[maxn];
set<int> mp;
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
maxx = 1;
mp.clear();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) color[i] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
set<int>::iterator iter = mp.upper_bound(a[i]);
if(iter != mp.end()){
color[a[i]] = color[*iter] + 1;
maxx = max(maxx, color[a[i]]);
}
else
color[a[i]] = 1;
mp.insert(a[i]);
}
printf("%d\n", maxx);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
printf(i == n ? "%d" : "%d ", color[a[i]]);
putchar('\n');
}
}
|
后面找到$HACK$数据:
应该输出:
实际输出:
然后队友开始修$bug$,我口胡了个单调栈的做法,能够通过这种情况。
不过被另外一种极为相似的情况坑了。
此时代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define maxn 1000005
using namespace std;
int t, n, nc, maxx, maxc, ans[maxn];
int top, stk[maxn];
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--)
{
maxc = 0;
nc = top = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int tmp, flag = 0;
scanf("%d", &tmp);
if(tmp > maxx)
{
maxx = tmp;
top = 0;
nc = 0;
}
while(top && stk[top] > tmp)
{
top--;
flag = 1;
}
if(flag || (!top))
{
stk[++top] = tmp;
ans[i] = ++nc;
}
else
{
stk[++top] = tmp;
ans[i] = nc;
}
maxx = max(maxx, tmp);
maxc = max(maxc, nc);
}
printf("%d\n", maxc);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
printf("%d ", ans[i]);
putchar('\n');
}
}
|
$HACK$数据:
应该输出:
实际输出:
连挂好几发大家都有点慌,不过好在队友带来了修正后做法,终于切了这第二题…
后面比赛结束了,才发现这个做法其实就是经典的求$LIS$的$nlogn$做法。
队友做法具体是:维护一个$set$,存放一个最长的染色序列内的元素,每次遇到新元素,就在$set$里用$upper_bound$进行查找大于当前元素的第一个元素$K$。如果当前这个元素是最大的,就染色为$1$,否则是$color[k]+1$,这一段和上面是一样的。
不同的地方在于,怎么确定某些值要不要被插入$set$中。队友维护了一个$map$,用于将染色的颜色编号映射到到染了这种颜色的最大权值的数。
如果当前染了的颜色是$map$里没有的,就添加。
如果当前染了的颜色是$map$里有的,并且当前的值比$map$里的大,就覆盖掉。
即:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| if(!maxcolor.count(color[a[i]]))
{
maxcolor[color[a[i]]] = a[i];
pre.insert(a[i]);
}
else if(maxcolor[color[a[i]]] < a[i])
{
pre.erase(maxcolor[color[a[i]]]);
maxcolor[color[a[i]]] = a[i];
pre.insert(a[i]);
}
|
其他部分一样,然后就可以$AC$该题。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define maxn 1000005
using namespace std;
int t, n, maxx, a[maxn], color[maxn];
set<int> pre;
map<int, int> maxcolor;
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--)
{
maxx = 1;
pre.clear();
maxcolor.clear();
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
set<int>::iterator iter = pre.upper_bound(a[i]);
if(iter == pre.end())
color[a[i]] = 1;
else
color[a[i]] = color[*iter] + 1,
maxx = max(maxx, color[a[i]]);
if(!maxcolor.count(color[a[i]]))
{
maxcolor[color[a[i]]] = a[i];
pre.insert(a[i]);
}
else if(maxcolor[color[a[i]]] < a[i])
{
pre.erase(maxcolor[color[a[i]]]);
maxcolor[color[a[i]]] = a[i];
pre.insert(a[i]);
}
}
printf("%d\n", maxx);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
printf("%d ", color[a[i]]);
putchar('\n');
}
}
|
Parallel Sort
一道思维题。
和上一题一样,又是给出了一个排列,考虑排列的特殊性质…
然后这题比赛结束也没搞出来…有点像上一次的ARC111-C Too Heavy。
后面看了题解,发现这道题存在一种至多两次就可以达到要求的构造方法。
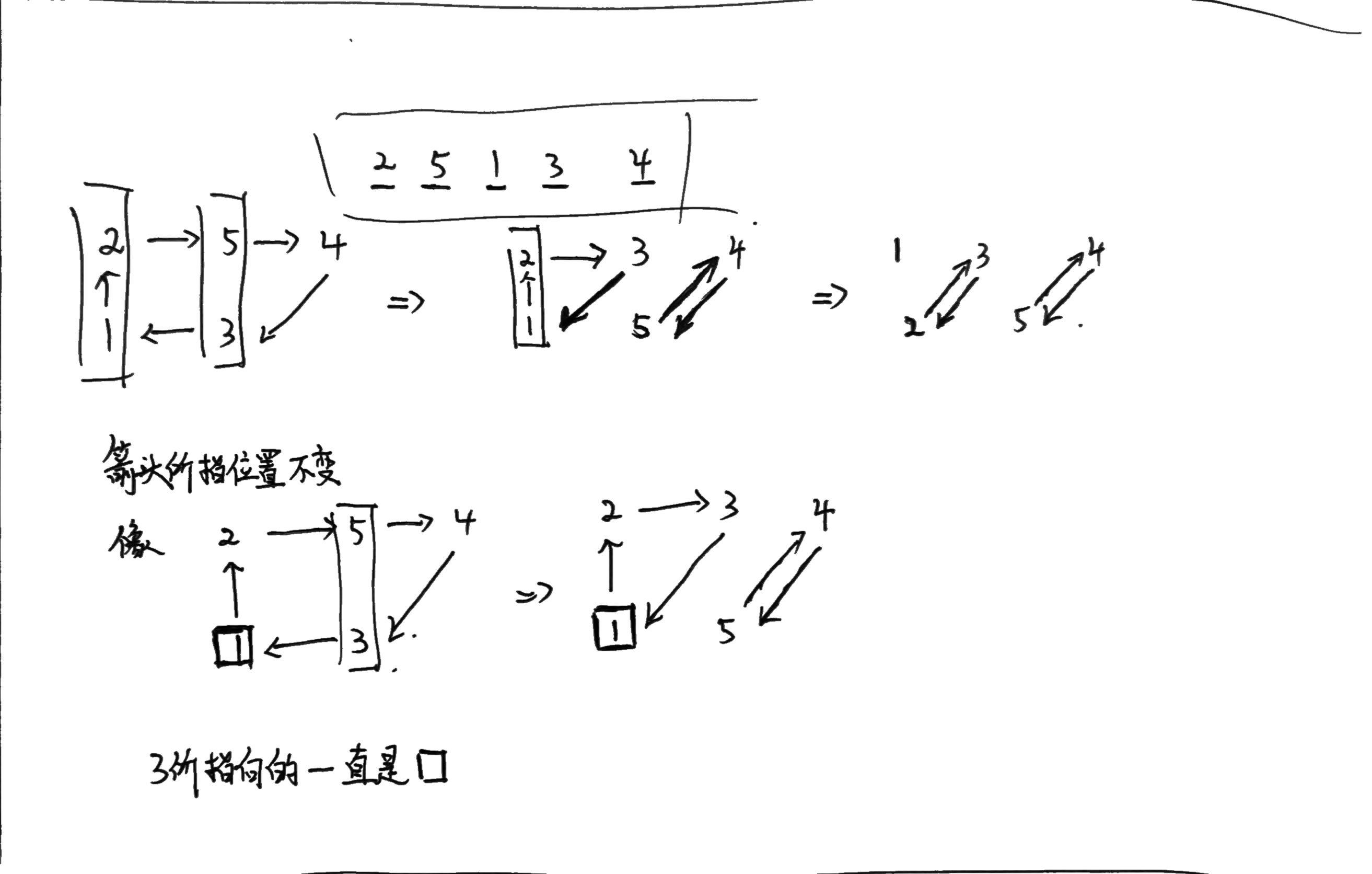
首先明确,对$a[i]->a[a[i]]->\dots$间连边,进行交换,思路和上面是一样的,能够产生若干个环,这些环间互不影响。
然后,考虑三种情况:
- 只有一个元素$a[i] = i$,已经在原位置了,跳过
- 环内有两个元素,经过一次交换就可以完成
- 环内有超过两个元素,经过多次交换才可以完成
但是,当环内有超过两个元素时,存在一种拆环的方法,可以将一个大环全部拆成前两种情况。
原因见下图(没带数位板,写草稿上拍的照片…):
还可以看这个大佬写的第45届ICPC亚洲区域赛昆明赛区 个人题解与心得 - 哔哩哔哩专栏 (bilibili.com)。
他用交换出边的解释来描述这个算法。
有了算法写代码就不难了。
代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
| #include <bits/stdc++.h>
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
using namespace std;
int n, p[maxn], vis[maxn];
vector<int> df, ans1, ans2;
void dfs(int x){
vis[x] = true;
df.push_back(x);
if(vis[p[x]])
{
int lf = 0, rt = df.size() - 1;
while(lf < rt)
{
ans1.push_back(df[lf]);
ans1.push_back(df[rt]);
swap(p[df[lf]], p[df[rt]]);
lf++; rt--;
}
df.clear();
return;
}
dfs(p[x]);
}
void dfs2(int x){
vis[x] = true;
df.push_back(x);
if(vis[p[x]])
{
int lf = 0, rt = df.size() - 1;
while(lf < rt)
{
ans2.push_back(df[lf]);
ans2.push_back(df[rt]);
swap(p[df[lf]], p[df[rt]]);
lf++; rt--;
}
df.clear();
return;
}
dfs2(p[x]);
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", &p[i]);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if(vis[i] || p[i] == i)
continue;
dfs(i);
}
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if(vis[i] || p[i] == i)
continue;
dfs2(i);
}
if(!ans1.size())
printf("0\n");
else if(!ans2.size())
printf("1\n");
else
printf("2\n");
if(ans1.size())
{
printf("%d", ans1.size() / 2);
for(int i = 0; i < ans1.size(); i += 2)
printf(" %d %d", ans1[i], ans1[i + 1]);
putchar('\n');
}
if(ans2.size())
{
printf("%d", ans2.size() / 2);
for(int i = 0; i < ans2.size(); i += 2)
printf(" %d %d", ans2[i], ans2[i + 1]);
putchar('\n');
}
}
|
别的
我是菜狗。
